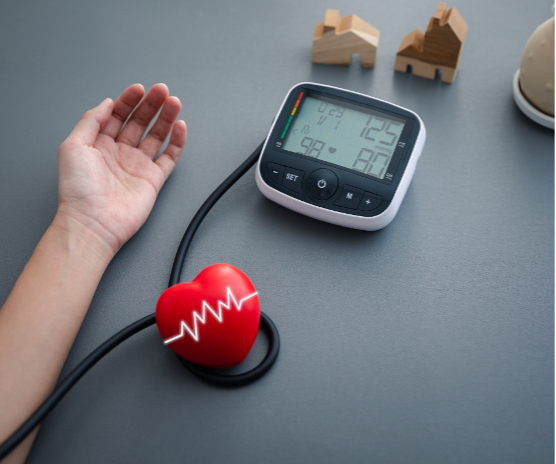
Breaking News Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well The Vital Role of Blood Pressure Monitoring and How to Do It Right Strategic Goals for Diabetic Patients: Maximizing Benefits from Diabetes Medications Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well Diabetic Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Guide to Signs, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Hypertension: Understanding the Silent Killer Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Obesity: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Facebook-f Instagram Twitter Pinterest-p Vimeo-v Za Pharmacy Drugs, Supplies and Delivery Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages More than 2 results are available in the PRO version (This notice is only visible to admin users) Why Blood Pressure Monitoring Matters Silent Threat: Hypertension frequently presents no symptoms. Over 46% of adults with high BP are unaware, according to the CDC. Preventable Risks: Early detection allows lifestyle adjustments (diet, exercise) or medical treatment, reducing complications. Tracking Trends: Consistent monitoring identifies patterns, helping differentiate temporary spikes from chronic issues. White Coat Syndrome: Home measurements can mitigate anxiety-induced highs common in clinical settings. Understanding the Numbers Normal: Below 120/80 mmHg Elevated: 120-129/<80 mmHg Hypertension Stage 1: 130-139/80-89 mmHg Hypertension Stage 2: 140+/90+ mmHg Consult a doctor if readings persist above 130/80 (per American Heart Association guidelines). How to Measure Blood Pressure Accurately Preparation: Rest: Sit quietly for 5 minutes. Avoid caffeine, smoking, or exercise 30 minutes prior. Bladder: Empty your bladder to prevent false highs. Position: Sit upright with back support, feet flat, and legs uncrossed. Rest your arm on a table at heart level. Cuff Placement: Use a validated, automated upper-arm monitor. Ensure the cuff fits—wrap it snugly around bare skin (not over clothing). The bottom edge should sit 1 inch above the elbow crease. During Measurement: Stay still and silent. Press start, and let the device inflate. Take two readings 1–2 minutes apart, then average them. Measure at the same time daily (e.g., morning and evening). Post-Measurement: Record readings with date/time. Share logs with your healthcare provider. Common Mistakes to Avoid Incorrect Cuff Size: Too small/tight inflates readings; too large underestimates. Arm Position: Hanging or unsupported arms alter results. Talking or Moving: Distorts accuracy. Skipping Calibration: Validate home devices annually. When to Seek Help Consult a doctor if: Readings consistently exceed 130/80 mmHg. You experience dizziness, headaches, or vision changes. Home/clinic readings differ significantly Conclusion Blood pressure monitoring is a simple yet lifesaving habit. By mastering proper technique and avoiding pitfalls, you gain insights into your health, enabling proactive care. Pair regular checks with heart-healthy choices—reduce sodium, stay active, manage stress—and partner with your healthcare team. Remember: Knowledge is power, and a few minutes with a cuff can safeguard your future. Check your numbers today—your heart will thank you. Sources: American Heart Association, CDC, Mayo Clinic. Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Engage Further: Share your BP tracking tips in the comments or explore our heart-healthy recipe section! This structured, actionable guide balances clarity with depth, encouraging readers to prioritize BP checks while equipping them with practical steps. Bullet points and subheadings enhance readability, making complex information accessible Blood Pressure Monitoring Blood pressure (BP) is a critical indicator of cardiovascular health, yet millions remain unaware of their numbers. Often dubbed the “silent killer,” hypertension can stealthily damage organs, escalating risks of heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. Regular monitoring empowers early detection and intervention, potentially saving lives. This article explores why BP checks matter and how to measure it accurately
Strategic Goals for Diabetic Patients: Maximizing Benefits from Diabetes Medications
Breaking News Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well The Vital Role of Blood Pressure Monitoring and How to Do It Right Strategic Goals for Diabetic Patients: Maximizing Benefits from Diabetes Medications Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well Diabetic Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Guide to Signs, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Hypertension: Understanding the Silent Killer Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Obesity: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Facebook-f Instagram Twitter Pinterest-p Vimeo-v Za Pharmacy Drugs, Supplies and Delivery Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages More than 2 results are available in the PRO version (This notice is only visible to admin users) 1. Achieve Target Blood Sugar Levels The primary goal of diabetes medications is to stabilize blood glucose within a healthy range. Consistently high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) damages organs, while extreme lows (hypoglycemia) pose immediate risks. A1C Targets: Most adults aim for an A1C below 7% (per ADA guidelines), though individualized targets may vary. Fasting/Post-Meal Goals: Fasting glucose of 80–130 mg/dL and post-meal levels under 180 mg/dL. How Medications Help: Insulin & Sulfonylureas: Directly lower blood sugar. Metformin: Reduces liver glucose production and improves insulin sensitivity. DPP-4 Inhibitors/GLP-1 Agonists: Regulate post-meal spikes 2. Prevent or Delay Complications Uncontrolled diabetes increases risks of heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Medications play a critical role in safeguarding long-term health. Heart Protection: SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., empagliflozin) and GLP-1 agonists (e.g., semaglutide) reduce cardiovascular risks. Kidney Preservation: ACE inhibitors or ARBs (for blood pressure) and SGLT2 inhibitors slow kidney damage. Nerve & Eye Health: Tight glucose control prevents diabetic neuropathy and retinopathy 3. Manage Weight Effectively Weight management is crucial, as obesity exacerbates insulin resistance. Certain medications aid weight loss, creating a positive cycle for glucose control. GLP-1 Agonists: Drugs like liraglutide suppress appetite and promote satiety. SGLT2 Inhibitors: Promote calorie loss through excess glucose excretion in urine. Avoid medications that cause weight gain (e.g., older sulfonylureas, insulin in excess doses). 4. Enhance Insulin Sensitivity For Type 2 diabetes, improving the body’s response to insulin is key. Metformin: First-line therapy for insulin resistance. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Activate insulin-sensitive genes (e.g., pioglitazone). 5. Minimize Hypoglycemia Risk Some medications, like insulin and sulfonylureas, can cause dangerous blood sugar drops. Balancing efficacy with safety is vital. Newer Agents: GLP-1 agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors carry low hypoglycemia risk. Education: Learn to recognize symptoms (shaking, sweating, confusion) and treat lows with fast-acting carbs 6. Improve Quality of Life Diabetes can drain energy and cause stress. Medications should help patients feel better, not burdened. Reduce Symptoms: Stabilizing glucose curbs fatigue, frequent urination, and thirst. Simplify Routines: Long-acting insulin or once-weekly GLP-1 injections enhance adherence. Mental Health: Better control eases anxiety about complications 7. Personalize Treatment Plans No two patients are alike. Medications should align with individual needs: Age & Lifestyle: Younger patients may prioritize flexibility (e.g., insulin pumps), while older adults focus on simplicity. Comorbidities: Prioritize drugs that address multiple issues (e.g., GLP-1 agonists for heart disease + obesity). Cost & Access: Advocate for affordable options with your healthcare team 8. Support Lifestyle Changes Medications work best alongside diet and exercise. Some drugs amplify these efforts: Metformin: Enhances benefits of weight loss and activity. Insulin: Adjust doses to match carbohydrate intake and exercise routines 9. Regular Monitoring & Adjustments Goals evolve, and medications may need fine-tuning. Track Progress: Use glucose logs, CGM data, and lab results. Stay Proactive: Report side effects (e.g., nausea from metformin) to explore alternatives Key Takeaways for Success Adhere to Prescriptions: Skipping doses undermines progress. Pair with Healthy Habits: Medications aren’t a substitute for diet and exercise. Communicate Openly: Update your doctor on challenges or changes Conclusion Beyond Blood Sugar – A Holistic Vision Diabetes medications are tools to help patients reclaim their health, not just lower numbers. By focusing on these goals—stabilizing glucose, preventing complications, enhancing well-being, and personalizing care—patients can transform their relationship with diabetes. Collaborate closely with your healthcare team, stay informed, and remember: every small step toward these goals is a victory. Sources: American Diabetes Association (ADA), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Disclaimer: Always consult your healthcare provider before adjusting medications. Engage Further: Share your medication success story in the comments or explore our guide to diabetes-friendly meal planning! This article balances clinical accuracy with patient-centered advice, emphasizing actionable goals and the synergy between medications and lifestyle. Clear headings, bullet points, and relatable examples make complex concepts accessible, empowering readers to take charge of their diabetes journey Strategic Goals for Diabetic Patients Diabetes management is a lifelong journey that requires a blend of lifestyle changes, monitoring, and medication. While medications are a cornerstone of treatment, their true power lies in helping patients achieve specific, measurable goals that enhance health and quality of life. This article outlines the key objectives diabetic patients should aim for when using medications, empowering them to take control of their condition and thrive
Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well
Breaking News Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well The Vital Role of Blood Pressure Monitoring and How to Do It Right Strategic Goals for Diabetic Patients: Maximizing Benefits from Diabetes Medications Thriving with Diabetes: A Holistic Guide to Living Well Diabetic Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Guide to Signs, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Hypertension: Understanding the Silent Killer Type 1 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Obesity: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment Facebook-f Instagram Twitter Pinterest-p Vimeo-v Za Pharmacy Drugs, Supplies and Delivery Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages Home About Drugs Diabetes community Hypertension awareness Diseases Health articles Contact Languages More than 2 results are available in the PRO version (This notice is only visible to admin users) 1. Master Your Plate: Nutrition as Medicine A balanced diet is your first line of defense. Focus on foods that stabilize blood sugar while nourishing your body: Choose Complex Carbs: Opt for whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables (e.g., broccoli, spinach) over refined sugars and white bread. Prioritize Protein: Incorporate lean proteins like chicken, tofu, or fish to slow glucose absorption. Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil support heart health and satiety. Fiber-Rich Foods: Aim for 25–30g daily to improve glycemic control (berries, chia seeds, lentils). Pro Tip: Try the “plate method”: Fill half your plate with veggies, a quarter with lean protein, and a quarter with whole grains 2. Move Your Body: Exercise as a Tool Physical activity boosts insulin sensitivity and overall health: Aim for 150 Minutes Weekly: Brisk walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent choices. Strength Training: Build muscle mass with resistance exercises 2–3x/week to improve glucose metabolism. Stay Consistent: Even short walks after meals can lower post-meal blood sugar spikes 3. Monitor Smartly: Knowledge is Power Regular checks help you stay in control: Blood Glucose Tracking: Use a glucometer or CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitor) to identify patterns. A1C Goals: Work with your doctor to personalize targets (typically below 7% for many adults). Log Trends: Apps like MyFitnessPal or glucose journals can reveal how food, stress, and activity affect your levels 4. Mental Wellness: Nurture Your Mind Diabetes can take an emotional toll. Prioritize mental health: Stress Management: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing to reduce cortisol (a hormone that raises blood sugar). Seek Support: Join diabetes communities (online or in-person) to share experiences and reduce isolation. Celebrate Wins: Acknowledge small victories, like hitting a step goal or choosing a healthy snack 5. Sleep & Recovery: The Unsung Heroes Poor sleep disrupts blood sugar and hunger hormones: Aim for 7–9 Hours: Create a calming bedtime routine (e.g., reading, no screens). Address Sleep Apnea: Common in diabetes, it’s treatable with CPAP therapy or lifestyle changes 6. Build a Healthcare Team You don’t have to navigate this alone: Endocrinologist: Specializes in diabetes care. Dietitian: Tailors meal plans to your preferences and needs. Mental Health Professional: Helps manage diabetes burnout or anxiety 7. Navigate Social Situations with Confidence Dining Out: Check menus ahead, ask for substitutions (e.g., veggies instead of fries), and practice portion control. Alcohol Moderation: Limit intake and pair drinks with protein to avoid lows. Educate Loved Ones: Share how they can support you without judgment 8. Stay Informed & Adaptive New Innovations: Explore tools like insulin pumps, CGMs, or hybrid closed-loop systems. Annual Checkups: Screen for complications (eye, kidney, nerve health) to catch issues early 9. Embrace a Positive Mindset Reframe Challenges: View diabetes management as self-care, not a burden. Focus on Abundance: Instead of dwelling on restrictions, explore new recipes, activities, and hobbies Conclusion Your Journey to Empowerment Living well with diabetes is about balance, not perfection. By integrating these strategies into your daily life, you’ll not only manage your blood sugar but also enhance your energy, mood, and longevity. Remember, every small choice adds up—whether it’s a walk around the block, a mindful meal, or a moment of self-compassion. You have the power to thrive. Sources: American Diabetes Association (ADA), CDC, Mayo Clinic. Disclaimer: Consult your healthcare team before making changes to your management plan. Engage Further: Share your favorite diabetes-friendly recipe or a tip that’s helped you live well in the comments below! This article blends actionable advice with a motivating tone, emphasizing that diabetes management is a journey of self-empowerment. Clear subheadings, bullet points, and relatable examples make it accessible, while highlighting the importance of physical, mental, and social well-being Thriving with Diabetes Living with diabetes doesn’t mean merely surviving—it means thriving. With the right strategies, you can manage your condition while enjoying a vibrant, fulfilling life. Diabetes requires daily attention, but it also empowers you to prioritize your health in ways that benefit your entire well-being. This guide offers practical, evidence-based tips to help you navigate nutrition, fitness, mental health, and more, transforming diabetes management into a pathway to resilience and vitality